LOCATION! LOCATION! LOCATION!
DID YOU KNOW…
The LOCATION (LOBE) of injury determines SYMPTOMS,
and that determines the THERAPY that will work best for you!
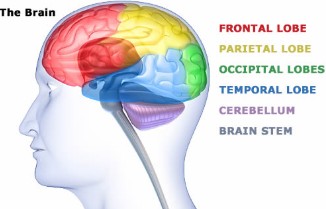

The LOCATION (LOBE) of injury determines SYMPTOMS,
and that determines the THERAPY that will work best for you!

Symptoms/THERAPY
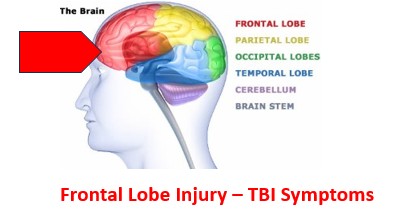
-Headaches, Dizziness, Anxiety
-Attention & Memory problems
– -Irritability, Poor Judgment
-COGNITIVE GAMES- LOGIC PUZZLES
-MOVEMENT-BASED THERAPY (Yoga, Tai Chi)
Symptoms/THERAPY
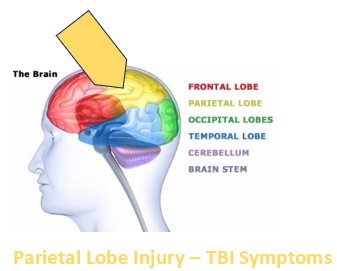
–Spatial awareness, coordination issues
-Motor skills, neglect 1 side of body
-Sensory, math /reading/writing
-MATH/LANGUAGE APPS
-SENSORY INTEGRATION T X
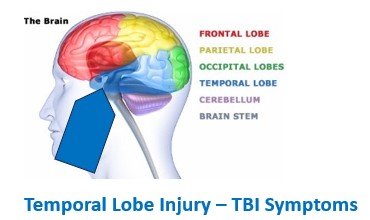
Symptoms/THERAPY
-Memory Loss, Difficulty following a conversation
-Auditory/Visual Processing Issues
-Emotional Flooding, Flashbacks
–MUSIC & SPEECH THERAPY
-VIDEO JOURNAL
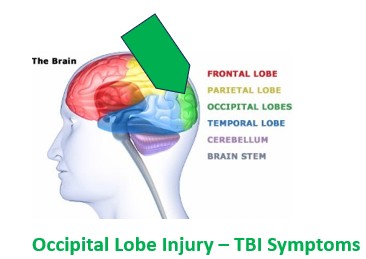
Symptoms/THERAPY
– Blurred/double vision; Visual field loss; Light sensitivity. Color confusion. Difficulty recognizing faces.
-LOW STIMULATION ENVIRONMENTS
-VISION RE-TRAINING
– ART THERAPY
These symptoms can vary in severity depending on the extent of the injury.
If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention and consult with a healthcare professional.
TBI 101: Behavioral & Emotional Symptoms | BrainLine
Frontal Lobe Damage: Symptoms, Treatment, & Recovery
Long-Term Effects of Traumatic Brain Injury | University of Utah Health
Here are some excellent resources and websites that can complement the self-rehabilitation therapies for TBI recovery. These will provide additional guidance and support for anyone navigating a TBI Recovery Journey:
General TBI Recovery Resources
Therapy and Rehabilitation
Community and Emotional Support
Educational and Informational Resources